The Most Dangerous Drug in Canada Is Not Prescription Opioids
/By Pat Anson
The most dangerous drug in Canada doesn’t require a prescription. You can’t smoke, vape, snort, or inject it. It doesn’t come in a pill, patch or edible.
It’s responsible for as many as 18-thousand deaths every year in Canada and can result in a lifetime of addiction. It ruins marriages, families, friendships and careers, and costs society about $20 billion a year in added healthcare expenses and lost productivity.
Yet it is readily available in most stores and can be purchased by anyone over the age of 19. In some provinces, the age limit is 18.
By now you’ve probably guessed that I’m talking about alcohol.
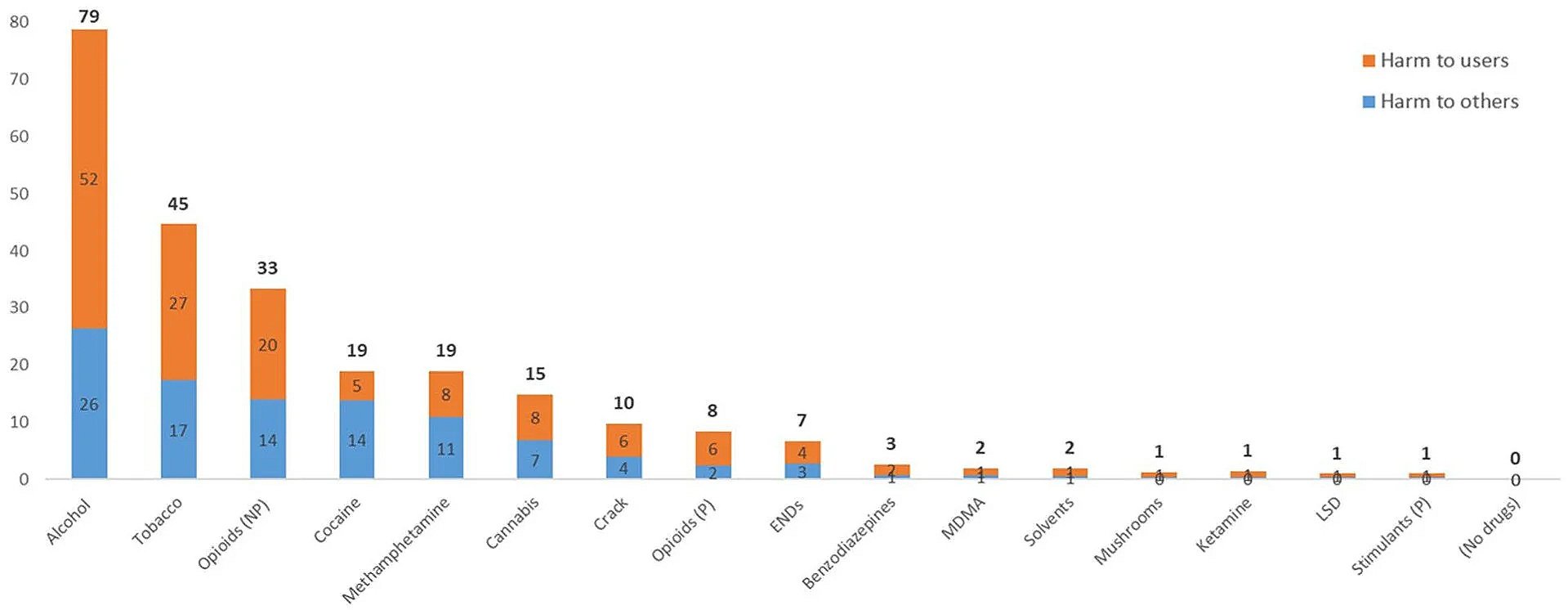
A new report by the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) found that alcohol causes more harm in Canada overall than any other drug — ranking well above tobacco, illicit fentanyl, cocaine, cannabis, methamphetamine and, yes, prescription opioids.
CAMH put together a diverse panel of 20 experts in public health, epidemiology, addiction, criminology, psychology and public policy to assess the short and long-term impact of 16 commonly used psychoactive drugs. In addition to the direct “harm to users” – such as addiction and overdose – they evaluated the indirect “harm to others” – families, communities and society at large.
“This is the first time this approach has been used to assess drug harms in Canada, and it gives us a much more complete picture than we had before,” said Jean-François Crépault, Senior Policy Advisor at CAMH and lead author of the study published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology.
“When we look at harm to people who use drugs and harm to others together, alcohol clearly stands out. Our findings highlight a major gap between the harms linked to alcohol and the way it is currently regulated in Canada.”
Based on a ranking system of 0 to 100, with zero meaning no harm and 100 being the most harmful, alcohol was given a score of 79, followed by tobacco (45) and non-prescription opioids (33). The latter category includes illicit fentanyl, xylazine, and other opioid-based street drugs.
Cocaine (19), methamphetamine (19), cannabis (15) and crack (10) are next, with “prescription opioids” (8) ranked as the eighth most harmful drug category.
Even that ranking is a bit misleading, as it includes morphine, oxycodone and other pharmaceutical opioids that are diverted and used without a prescription – which probably should be counted as non-prescription opioids.
Prescription opioids were ranked so low in terms of harm, they barely beat out ENDs (7), an acronym for electronic nicotine delivery systems, more commonly known as vapes or e-cigarettes.
Most Harmful Drugs in Canada
JOURNAL OF PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY
The finding that alcohol causes the most harm aligns with previous studies in the United Kingdom, the European Union, Australia and New Zealand.
In the United States, a recent study that used a slightly different methodology ranked alcohol as the 5th most harmful drug, behind illicit fentanyl, methamphetamine, crack and heroin. Prescription opioids ranked as the 7th most harmful drug in the U.S.
Experts say these studies point to a clear need for government drug policies to better align with the actual harm that a specific drug causes – and not be based on laws, guidelines, class action lawsuits, or whatever drug hysteria is popular at the moment.
Despite all the harm it causes, no one talks about banning alcohol, yet natural leaf kratom and the kratom extract 7-OH are being demonized as “gas station heroin” and “legal morphine” that should be banned. Never mind that there is little solid evidence they are dangerous when used appropriately. Neither substance made the “harmful” list in Canada, United States, or anywhere else.
“The key message here is that harm is not just about what a drug does to the body,” said Crépault. “How a drug is regulated shapes who uses it, how it is used, and how much harm it causes. Evidence-based policy can significantly reduce harm, and governments have a real opportunity to use regulation to protect public health.”