By Dr. Forest Tennant, PNN Columnist
In 1896, Dr. Henry Snow was the chief cancer surgeon at the Royal Brompton Hospital in London. He recognized and agonized over the immense pain and suffering of his patients when they developed constant pain and approached their end of life.
Dr. Snow wanted to relieve their suffering, so he administered the drugs that were available one at a time: morphine, cocaine and alcohol. With each he managed to get some pain relief, but didn’t obtain the relief he wanted and patients were still suffering. Not to be deterred, he made a profound discovery.
Dr. Snow mixed morphine and cocaine in liquid alcohol and administered the solution to his patients. Then he found formidable and humane pain relief. This three-drug mixture gave rise to the concept of “synergy of constituents,” which means that the simultaneous administration of multiple pain-relieving drugs added up to more than each one alone. In other words, two and two equaled six rather than four.
The success of Dr. Snow’s discovery spread rapidly to other hospitals and countries, and became known as the “Brompton cocktail.” In France and elsewhere, physicians discovered they could add an antihistamine, antipsychotic or cannabis oil to the mixture and get even more pain relief.
The Brompton cocktail was used until the 1970’s, when it gave way to the convenience of opioid tablets, capsules and injections, rather than the time and cost of making a liquid that contained multiple drugs.
The Amphetamine Discovery
Fortunately, after the demise of the Brompton cocktail, a handful of researchers weren’t about to forget the “synergy of constituents” and the pain-relieving potency of stimulants like cocaine. An example of the pain-relieving capability of stimulants is caffeine, which in the 1960’s was added to a variety of pain relievers such as aspirin and codeine to obtain synergy.
Amphetamine was discovered in the 1930’s and promoted as “Benzedrine” to stay awake while driving. Because amphetamine produced alertness, it became known as a stimulant. Clinical reports began to surface in the 1940’s that amphetamine and its derivatives also helped depression, weight loss, mental alertness, hyperactivity and attention span. They soon began to be marketed and labeled for those conditions.
Clinical studies on amphetamine derivatives for pain relief were finally started in the 1980’s, and they clearly showed that they provided a great deal of pain relief.
By the time the last century folded, a core of pain researchers knew that not only cocaine but amphetamine derivatives such as methylphenidate and phentermine relieved pain. What they didn’t know was why. This answer was to come 15-20 years later.
Stimulants Initially Rejected
I became quite excited about the clinical trials that showed stimulants relieved pain, and in the late 1990’s gave a group of intractable pain patients the weak stimulant and weight loss drug phentermine, in combination with clonidine. The opioid dosages for these patients dropped 40 to 50 percent within six weeks and they got even better pain relief.
I presented my findings to colleagues at some national professional meetings. Much to my surprise, I was summarily informed that the new long-acting opioid formulations of the fentanyl patch (Duragesic), oxycodone (Oxycontin), morphine (MS Contin) and the implanted intrathecal (spine) opioid pump eliminated any need for stimulants or the concept of “synergy of constituents.”
By the turn of the century, the use of these new long-acting opioids and implanted opioid pumps became the standard of the day. Stimulants and their synergy were essentially forgotten, and they were rarely used for intractable pain again until about 2010.
The Rebirth of Synergy
After the year 2000, I don’t recall ever being referred an intractable pain patient who had not already been started on one of the long-acting opioids and/or an implanted opioid pump. They were referred to me simply because they were not getting adequate pain relief. Almost every one of these patients had found that their opioids quit working well, regardless of dosage or even if a second or third opioid was added to the mix.
Somewhat out of desperation, about 12 years ago I recalled Dr. Snow, the Brompton cocktail and the “synergy of constituents.” I also remembered my study on phentermine and clonidine, so I started giving patients on opioids who were doing poorly my favorite stimulant, phentermine, or occasionally methylphenidate (Ritalin).
Later the narcolepsy drug modafinil (Provigil) and a mixture of amphetamine salts (Adderall), came on the market. They too proved to be excellent “synergists” with opioids. I found that every intractable pain patient who received one of these stimulants not only got better pain relief and were either able to “hold the line” or reduce their opioid dosage.
Phentermine continued to be my favorite stimulant to relieve pain and reduce the use of opioids because it additionally kept weight down and helped the patient keep moving and functional.
Why Stimulants Work
Although stimulants have been clinically known to relieve pain since Dr. Snow’s experiments in 1896, researchers didn’t provide us with the biologic “why” until recently.
In the past decade, some outstanding researchers determined that there are about half a dozen different neurotransmitters in the brain and spinal cord that relieve pain. The three major neurotransmitters are endorphin, dopamine and gamma amino butyric acid (GABA). These neurotransmitters relieve pain by activating trigger points in the central nervous system called receptors.
These astute researchers also determined that intractable pain may deplete endorphin, dopamine and GABA. Consequently, a substitute drug may have to be administered to obtain adequate pain relief.
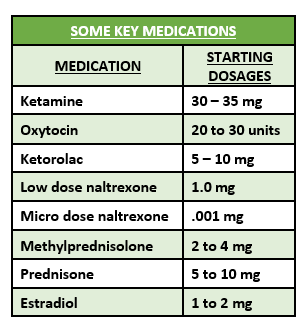
If you have constant, intractable pain, you may likely need the “synergy of constituents,” which will include an opioid, stimulant, and GABA substitute. Popular GABA substitutes include diazepam (Valium), carisoprodol (Soma), pregabalin (Lyrica), gabapentin (Neurontin), clonazepam (Klonopin), topiramate (Topomax) and alcohol.
Which Patients Should Receive a Stimulant?
Stimulants have well-known abuse and addiction potential, so they should only be given to patients who have a well-documented disease or injury that is known to cause severe intractable pain. The most common diseases in this category are adhesive arachnoiditis, stroke or head trauma, reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD/CRPS), Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, and some autoimmune-collagen disorders.
In most cases, patients who need a stimulant are clearly debilitated and require some family and caretaker support to function and carry out activities of daily living.
Intractable pain patients have several dopamine substitutes available:
Misunderstood Objections
Many medical practitioners are not yet aware of the new research on stimulants and hesitate to prescribe them, even to needy, legitimate patients. The fear of abuse, diversion or dependence by the intractable pain or palliative care patient, while understandable, should not cause reluctance to prescribe a stimulant to these patients. No intractable pain patient will give away something that works so well.
In addition, the dosage of stimulants for pain relief is considerably lower than the usual level needed for abuse. Only small dosages are clinically needed in most cases and pharmacies today only issue limited quantities. Another safety factor in controlling adverse consequences of stimulants is that the severe intractable pain patient will usually have close family or caretaker support who can safely store and administer stimulants.
There is an unfounded fear of hypertension if a stimulant is prescribed. This is rarely the case, since the pain patient is dopamine deficient. A stimulant drug in an intractable pain patient may actually lower blood pressure since it may be elevated due to pain.
There is the belief that Adderall, Ritalin and some other stimulants are only for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). What is misunderstood is that ADHD is universal among intractable pain patients. Every person with intractable pain has reduced attention span, hypertension and agitation. One could argue that every intractable pain patient should be on a stimulant just for their ADHD.
Dr. Snow and the Royal Brompton Hospital had the right idea. The severe, intractable pain patient needs an opioid to replace endorphin, a stimulant to replace dopamine, and a substitute for GABA.
It’s time we bring back the “synergy of constituents” to humanely get better pain relief and simultaneously lower opioid dosages in the intractable pain patient.
Forest Tennant, MD, DrPH, is retired from clinical practice but continues his studies on the treatment of intractable pain through the Arachnoiditis Research and Education Project. A bibliography on stimulants for intractable pain treatment can be found here
The Tennant Foundation gives financial support to Pain News Network and sponsors PNN’s Patient Resources section.