Misuse of Pain Meds by Teens Continues Decline
/By Pat Anson, Editor
Two new studies this week paint a somewhat conflicting picture about the abuse of opioids by teens and pregnant women.
A survey of over 45,000 teens by the University of Michigan and the National Institutes of Health found that teenage drug abuse continues to decline, with a significant drop in the misuse of the painkiller Vicodin. A second study at the university found the number of babies born with opioid withdrawal symptoms has grown substantially, especially in rural areas.
The annual Monitoring the Future survey found that 4.8% of high school seniors had misused an opioid pain reliever in the past year, down from a peak of 9.5% in 2004. In the past five years alone, misuse of opioid pain medication by 12th graders has declined by 45 percent.
Only 2.9% of high school seniors reported the misuse of Vicodin in 2016, compared to nearly 10 percent a decade ago. Vicodin and other hydrocodone products were reclassified as Schedule II controlled substances in 2015, making them harder to obtain.
"Clearly our public health prevention efforts, as well as policy changes to reduce availability, are working to reduce teen drug use,” said Nora Volkow, MD, director of National Institute of Drug Abuse.
The survey found a continued long-term decline in teenage use of many illicit substances, as well as alcohol and tobacco. The use of any illicit drug was the lowest in the survey’s history for eighth graders. One negative sign was an increase in the misuse of over-the-counter cough medicine by eighth graders.
Marijuana use in the past month by eighth graders fell to 5.4%, down from 6.5% in 2015. However, among high school seniors, nearly one in four reported marijuana use in the past month. There also continues to be a higher rate of marijuana use in the past year (38%) among 12th graders in states with medical marijuana laws.
"It is encouraging to see more young people making healthy choices not to use illicit substances," said National Drug Control Policy Director Michael Botticelli. "We must continue to do all we can to support young people through evidence-based prevention efforts as well as treatment for those who may develop substance use disorders.”
The majority of teens continue to say they get most of their opioid pain relievers from friends or relatives, either stolen, bought or given. The only prescription drugs seen as easier to get in 2016 than last year are tranquilizers, with 11.4 percent of eighth graders reporting they would be “fairly easy” or “very easy” to get.
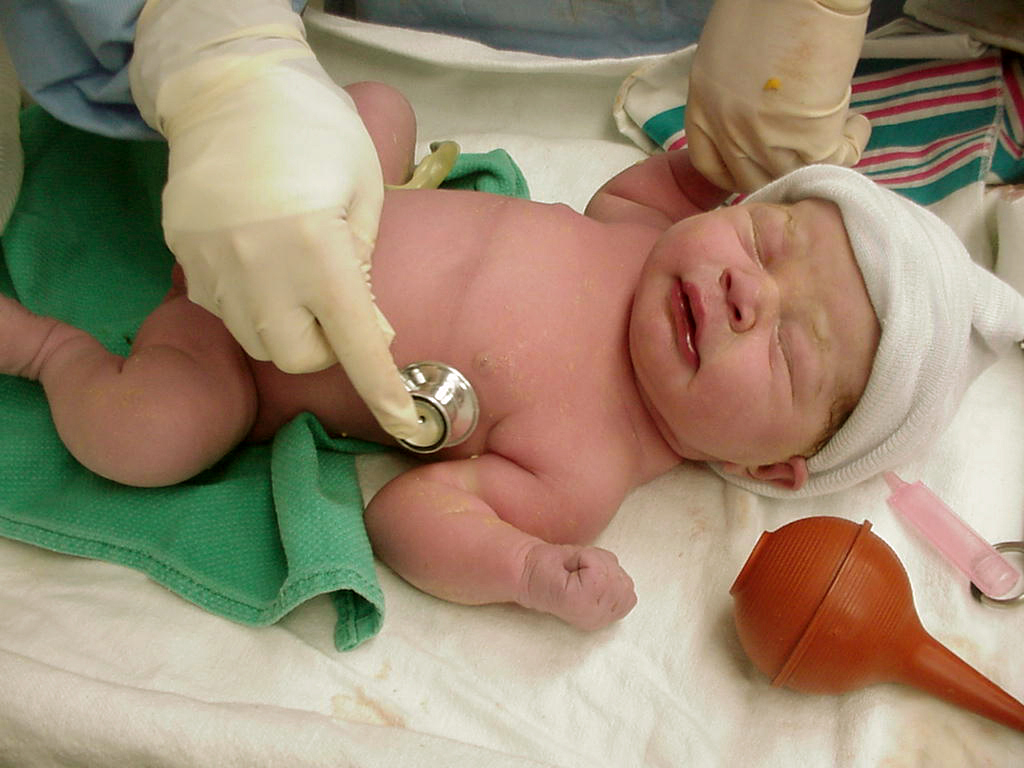
More Babies Suffering from Opioid Withdrawal
The number of babies born with drug withdrawal symptoms from opioids grew substantially faster in rural communities than in cities, according to the University of Michigan study. The study did not distinguish between opioid pain medication and illegal opioids such as heroin.
Newborns exposed to opioids in the womb and who experience withdrawal symptoms after birth (neonatal abstinence syndrome) are more likely to have seizures, low birthweight, breathing, sleeping and feeding problems.
Researchers found that in rural areas, the rate of newborns diagnosed with neonatal abstinence syndrome increased from nearly one case per 1,000 births from 2003-2004 to 7.5 cases from 2012-2013. That's a surge nearly 80% higher than the growth rate of such cases in urban communities.
"The opioid epidemic has hit rural communities especially hard and we found that these geographical disparities also affect pregnant women and infants," says lead author and pediatrician Nicole Villapiano, MD, whose study was published in JAMA Pediatrics.
Using national data, researchers found that rural infants accounted for over 21 percent of all infants born with neonatal abstinence syndrome. In 2003, rural infants made up only 13 percent of the neonatal abstinence syndrome cases in the U.S.
Maternal use of opioids in rural counties was nearly 70 percent higher than in urban counties. Rural infants and mothers with opioid-related diagnoses were more likely to be from lower-income families, have public insurance and be transferred to another hospital following delivery.
Villapiano says families in urban areas typically have better access to addiction treatment programs.
"We need to consider what kind of support moms with opioid disorders have in rural communities," she said.
Villapiano suggests that increasing the number of rural doctors authorized to prescribe the addiction treatment drug buprenorphine (Suboxone), as well as expanding rural mental health and substance abuse services, would be good first steps in reversing the trend in neonatal abstinence syndrome.