Research Links Auto Plant Closures to Opioid Overdoses
/By Pat Anson, PNN Editor
A new study is adding to the growing body of evidence linking the opioid crisis to unemployment, depression, suicide and declining economic opportunities – the so-called epidemic of despair.
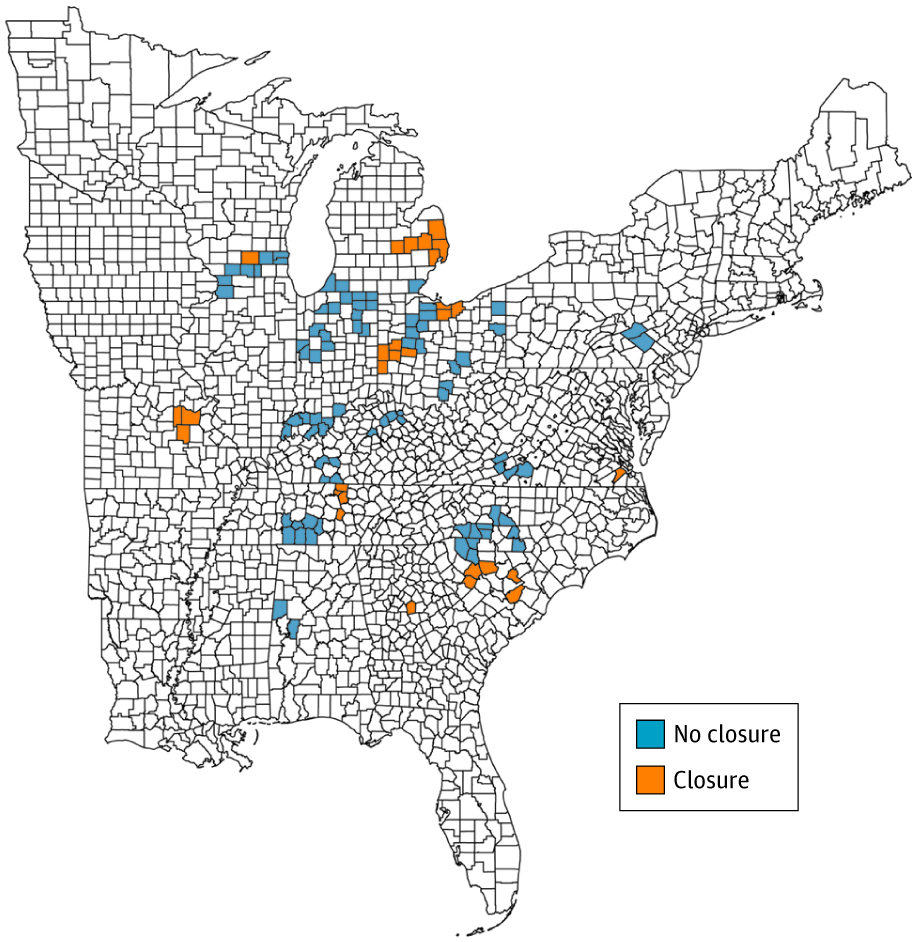
Researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and Massachusetts General Hospital looked at the closure of automotive assembly plants in the U.S from 1999 to 2016, primarily in the Midwest and Southeast. They found that opioid overdoses rose significantly in 29 counties where an auto plant shutdown.
Five years after the plants closed, opioid overdose rates among adults were 85 percent higher in counties where closures occurred compared to 83 counties where plants remained open.
"Major economic events, such as plant closures, can affect a person's view of how their life might be in the future. These changes can have a profound effect on a person's mental well-being, and could consequently influence the risk of substance use," said lead author Atheendar Venkataramani, MD, an assistant professor of Medical Ethics and Health Policy.
"Our findings confirm the general intuition that declining economic opportunity may have played a significant role in driving the opioid crisis."
The findings are published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
The demographic group with the biggest increase in opioid overdose deaths after an auto plant closure was non-Hispanic white men between 18-34 years old, followed by non-Hispanic white men ages 35-65 years old. Opioid overdose rates also increased among young non-Hispanic white women.
Death rates involving heroin and other illicit opioids were higher for young white men and women than for prescription opioids, while older white men were more likely to die from prescription opioids.
"While we as clinicians recognize and take very seriously the issue of overprescribing, our study reinforces that addressing the opioid overdose crisis in a meaningful way requires concurrent and complimentary approaches to diagnosing and treating substance use disorders in regions of the countries hardest hit by structural economic change," Venkataramani said.
“Our findings should not be interpreted in such a way as to diminish the role of opioid supply, either from physician prescriptions or from illicitly made and supplied synthetic substances, in the US opioid overdose crisis.”
Princeton researchers Anne Case and Angus Deaton were the first to suggest in 2015 that the declining life expectancy of Americans was not caused by drug abuse alone, but linked to unemployment, poor finances, lack of education, divorce, depression and loss of social connections. They estimate that nearly half a million white Americans died due to a quiet epidemic of pain, suicide, alcohol abuse and opioid overdoses.
The epidemic of despair has also been cited as one of the reasons for the election of Donald Trump and for a “syndemic” of overdoses occurring in counties where the opioid crisis first erupted, particularly in mid-sized cities in Kentucky, Ohio and West Virginia.