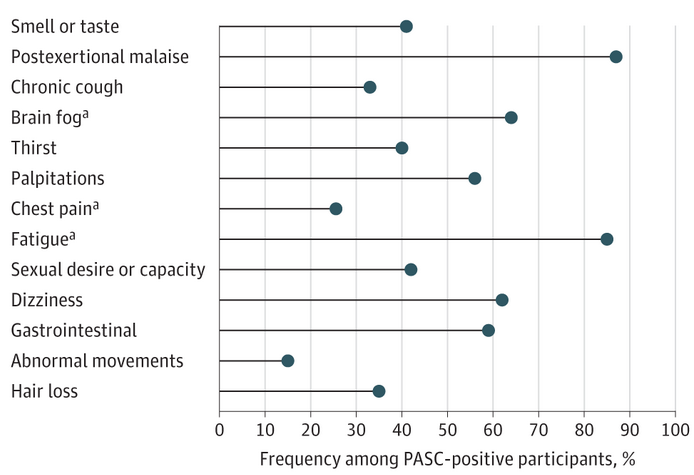
‘Game Changing’ Study Finds Cause of Long Covid Brain Fog
/By Pat Anson, PNN Editor
Inflamed and leaky blood vessels in the human brain appear to be the cause of brain fog and other cognitive issues in patients with Long Covid, according to a groundbreaking study by a team of Irish researchers.
The discovery that a viral infection may cause cognitive decline could help explain why memory loss, confusion and trouble concentrating is common in patients with other chronic illnesses, such as fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis and chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS).
Scientists at Trinity College Dublin and FutureNeuro used a specialized MRI to compare the brains of Long Covid patients with brain fog to those without brain fog.
The MRI images show how Long Covid can affect the brain’s delicate network of blood vessels. Patients with brain fog (right column) have significantly more inflammation and blood vessel leakage than those without brain fog (left column).
Patients with brain fog also had more elevated levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in their blood, which is a sign of cerebrovascular damage often found in patients with repetitive head trauma.
The images and findings are published in the journal Nature Neuroscience.
“For the first time, we have been able to show that leaky blood vessels in the human brain, in tandem with a hyperactive immune system, may be the key drivers of brain fog associated with Long COVID,” said lead author Matthew Campbell, PhD, a Professor in Genetics and Head of Genetics at Trinity College, and Principal Investigator at FutureNeuro.
“The concept that many other viral infections that lead to post-viral syndromes might drive blood vessel leakage in the brain is potentially game changing and is under active investigation by the team.”
NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
About 10% of the people infected with the SARS-CoV2 virus develop Long Covid, a broad range of conditions that causes fatigue, shortness of breath, and muscle and joint pain. About half of Long Covid patients also report brain fog or some lingering neurological issue.
“The findings will now likely change the landscape of how we understand and treat post-viral neurological conditions. It also confirms that the neurological symptoms of Long Covid are measurable with real and demonstrable metabolic and vascular changes in the brain,” said co-author Colin Doherty, Professor of Neurology and Head of the School of Medicine at Trinity, and Principal Investigator at FutureNeuro.
In recent years, research has found that multiple sclerosis, lupus and other autoimmune conditions are triggered by the Epstein-Barr virus. The exact mechanism is unclear and proving there is a direct link between viral infections and brain fog has been challenging – until now.
“Our findings have now set the stage for further studies examining the molecular events that lead to post-viral fatigue and brain fog. Without doubt, similar mechanisms are at play across many disparate types of viral infection and we are now tantalisingly close to understanding how and why they cause neurological dysfunction in patients,” said first author Chris Greene, PhD, a research fellow in the School of Genetics and Microbiology at Trinity.
The study was funded by Science Foundation Ireland, the European Research Council and FutureNeuro, a research center for chronic and rare neurological diseases.