Why U.S. Biologic Drugs Are So Expensive
/By Sarah Jane Tribble, Kaiser Health News
Europeans have found the secret to making some of the world’s costliest medicines much more affordable, as much as 80 percent cheaper than in the U.S.
Governments in Europe have compelled drugmakers to bend on prices and have thrown open the market for so-called biosimilars, which are cheaper copies of biologic drugs made from living organisms. The brand-name products — ranging from Humira for rheumatoid arthritis to Avastin for cancer — are high-priced drugs that account for 40 percent of U.S. pharmaceutical sales.
European patients can choose from dozens of biosimilars, 50 in all, which have stoked competition and driven prices lower. Europe approved the growth hormone Omnitrope as its first biosimilar in 2006, but the U.S. didn’t follow suit until 2015 with cancer-treatment drug Zarxio.
Now, the U.S. government stops short of negotiating and drugmakers with brand-name biologics have used a variety of strategies — from special contracting deals to overlapping patents known as “patent thickets”— to block copycat versions of their drugs from entering the U.S. or gaining market share.
As a result, only six biosimilars are available for U.S. consumers.
European countries don’t generally allow price increases after a drug launches and, in some cases, the national health authority requires patients to switch to less expensive biosimilars once the copycat product is proven safe and effective, said Michael Kleinrock, research director for IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science.
From $50 to $1,300 a month
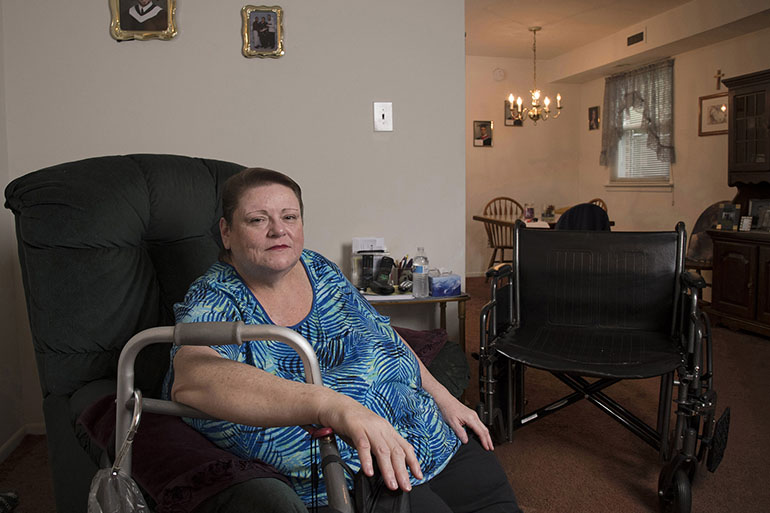
If Susie Christoff, a 59-year-old who suffers from debilitating psoriatic arthritis, lived in Italy, the cost of her preferred medicine would be less than quarter of what it is in the U.S., according to data gathered by GlobalData, a research firm.
Christoff tried a series of expensive biologics before discovering a once-a-month injection of Cosentyx, manufactured by Swiss drugmaker Novartis, worked the best.
Without the medicine, Christoff said, her fingers can swell to the size of sausages.
SUSIE CHRISTOFF (KAISER HEALTH NEWS PHOTO)
“It’s 24/7 constant pain in, like, the ankles and feet,” said Christoff, who lives in Fairfax, Va. “I can’t sleep, [and] I can’t sit still. I cry. I throw pillows. It’s just … awful.”
At first, Christoff’s copay for Cosentyx was just $50 a month. But when a disability led her to switch to a Medicare Advantage plan, her out-of-pocket costs ballooned to nearly $1,300 a month — more than three times her monthly car loan.
Christoff, with the help of her rheumatologist, Dr. Angus Worthing, tried Enbrel, Humira and other drugs before finding Cosentyx, the only drug that provides relief. Christoff’s case is “heartbreaking,” Worthing said.
Novartis declined to respond to questions about Cosentyx’s price. Instead, like other pharmaceutical companies, Novartis says it offers patient assistance programs for those who can’t afford the drug. Christoff said she doesn’t qualify for financial assistance.
Like other biologics, Cosentyx costs thousands of dollars per month. The annual cost of Christoff’s treatment runs about $65,000 in the U.S. In Italy, where competition and price negotiations play a bigger role, it would run about $15,000, according to GlobalData.
In England, Dr. Christopher Griffiths, a lead researcher at the National Institute for Health Research who treats patients with Cosentyx, said the National Health Service would pay about 10,000 pounds, or less than $13,000.
And those drastic price differences are true even though there is no biosimilar version of Cosentyx yet available in Europe, and might not be for years.
The cost of the drug is taking a toll on Christoff. This past summer, her progressive disease made it difficult to enjoy the annual family vacation with her three grown children and their kids in Virginia Beach, Va.
“I can’t get down on the sand to play with my kids without help. I can’t get up without help,” Christoff recalled. “I’m not ready to stop trying. But I’m also not ready to go through my entire retirement fund to walk.”
Unlike Cosentyx, rival drugs — Humira, Enbrel and Remicade — all face biosimilar competition in Europe. Only Remicade has competition from a lower-cost biosimilar in the U.S., and Humira isn’t expected to have a copycat competitor in the U.S. market until 2023. Humira, made by AbbVie, is the world’s top-selling drug.
In late October, Wall Street analyst Ronny Gal at Sanford C. Bernstein & Co. noted that AbbVie agreed to drop Humira’s price by 80 percent in one Nordic country to combat biosimilar competition. During the company’s quarterly conference call, AbbVie chief executive Richard Gonzalez said the drug’s discount was as low as 10 percent and as high as 80 percent across the continent, with the highest discounts in Nordic countries.
“These are markets where it’s ‘winner takes all’ across the entire… category, so includes Remicade and Enbrel as well,” Gonzalez said in November, adding that Nordic countries represent about 4 to 5 percent of overall revenue in AbbVie’s international business.
Concerned about how much biologics cost the U.S. health system and patients, Food and Drug Administration Commissioner Scott Gottlieb announced an “action plan” this summer that included tapping the Federal Trade Commission for help, saying he was “worried” about the biosimilar market.
“The branded drug industry didn’t build its success by being business naive; they are smart competitors,” Gottlieb told an audience full of advocates, industry insiders and researchers at the Washington, D.C.-based Brookings Institution in July. “But that doesn’t mean we need to embrace all of these business tactics or agree with them and think they are appropriate.”
Rebate Traps
One of these business tactics involves so-called rebate traps, in which financial deals are cut to make sure patients can get only a biologic, not a biosimilar. International drugmaker Pfizer alleged in a September 2017 lawsuit that exclusionary contracts created by Johnson & Johnson prevented use of its biosimilar by health insurers, hospitals and clinics.
Johnson & Johnson’s wildly successful biologic Remicade, the brand-name version of infliximab, produced $6.3 billion in worldwide in 2017. Pfizer launched its copycat drug, Inflectra, in the U.S. in October 2016, noting in the announcement that it would price the drug at a 15 percent discount to Remicade’s wholesale price.
Still, health systems such as Geisinger Health, based in Pennsylvania, say they have had difficulty switching to the less expensive alternative.
“J&J has done a really good job of entrenching themselves in the market,” said Jason Howay, manager of formulary services at Geisinger.
The health system ultimately decided it wanted to switch all adults to Pfizer’s biosimilar, saying it provided the same quality of treatment. But Johnson & Johnson had “bundled” the prices of other drugs with Remicade. So if Geisinger stopped using Remicade on adult patients, J&J could stop providing discounts on other drugs, such as those used for cardiology, Howay explained. “It weaves a very tangled web.”
A spokeswoman for Janssen, Johnson & Johnson’s main pharmaceutical subsidiary, says the drugmaker does offer “more attractive contract terms” to buyers who use a wider range of J&J medicines. “Our contracting approach has always prioritized access for patients and their providers,” Meredith Sharp says.
Geisinger negotiated with biosimilar maker Pfizer and won still lower prices to make up for lost savings on the other J&J drugs. It’s now transitioning all adult patients to the less expensive biosimilar.
Kaiser Health News, a nonprofit health newsroom whose stories appear in news outlets nationwide, is an editorially independent part of the Kaiser Family Foundation.